PEG tube insertion – discharge
PEG tube insertion – discharge
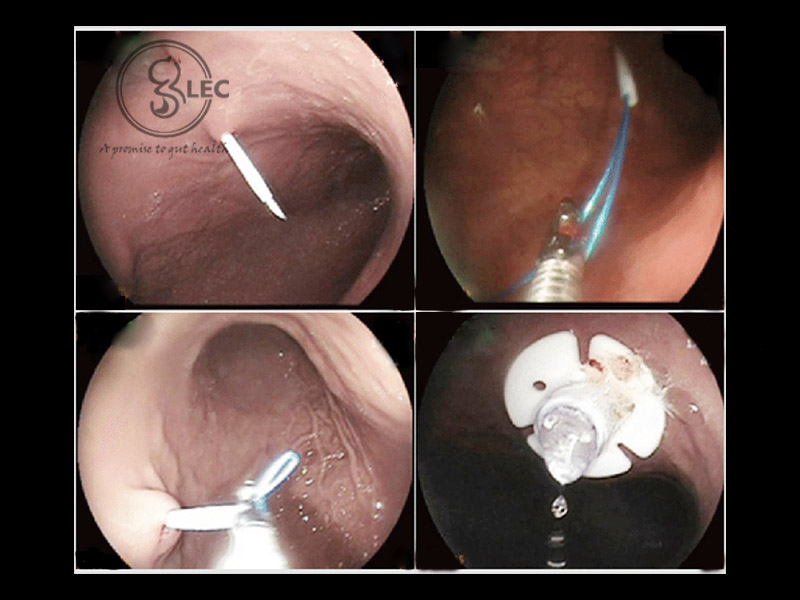
A PEG (percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy) feeding tube is the insertion of a feeding tube that extends to the stomach wall through the skin. It penetrates directly into the stomach. Endoscopy is helpful in directing the pathway of feeding tube.
Feeding tubes are indicated if a person is unable to eat or drink. For example, some medical conditions may cause this such as brain injury, or stroke. Others include head and neck surgery, problems with the esophagus, and other complications.
PEG tube is simple and easy to use.
It can be learned and an individual can care on their own to give tube feedings.
Components of PEG Tubes
PEG tube consists of parts such as:
- PEG/Gastrostomy feeding tube.
- 2 small discs present inside and outside of the gastrostomy opening, within the stomach wall. The discs maintain the position of the feeding tube.
- A clamp that closes the feeding tube.
- A device that maintains the position of the tube to the skin when feeding is not required.
Once the gastrostomy has been established for a while and opening (stoma) exists, a button device is fixed. It makes the feeding quick, manageable and simpler.
The tube consists of a mark that demonstrates where it leaves the stoma. This mark can be used to identify the correct position of the tube.
Things to take into consideration:
Certain factors should be taken into account during PEG placement:
- Signs or symptoms of infection
- Any sign of tube blockage and how to manage it
- How to maintain tube position
- How to place the tube under clothes
- How to use the tube for emptying the stomach
- What activities can be done and what to avoid
Feedings should be initiated with clear liquids, which can be later increased to solid foods slowly. The patient should be guided:
- How to use the tube to give yourself food or liquid
- How to maintain the tube
- How to use tube for taking medications
Maintenance of the PEG-tube Site
Drainage commonly occurs for 1-2 days around the tube. Skin healing takes 2-3 weeks.
- Skin around the tube should be cleaned 1-3 times/day.
- A mild soap and water/saline water can be used to clean with a gauze or cotton swab
- Gently remove any crusting around the tube and skin
- Dry the skin with a clean towel/li>
- Be gentle to not pull out the tube while takin care
During the initial 1-2 weeks, healthcare providers advise to use sterile technique to take care of the PEG-tube site.
A special absorbent pad or gauze may be required to be placed at the tube site. If the tube is not clean then appropriate care is required to keep it clean.
- Avoid heavy dressings.
- Do not place a gauze under the disc.
- Avoid any sprays, powders etc. if provider has not asked for it
- Ask the doctor when will it be ok to take shower
Positioning the PEG-tube in Place
- When the feeding tube comes out, the opening (stoma) may get closed. Thus, to prevent this the tube should be taped to the abdomen or use a fixation device.
- A new tube should be used immediately.
- Contact the provider and he will guide how to rotate the gastrostomy tube while cleaning.
- It helps to prevent the tube from sticking to the stoma.
Contact the Doctor if:
Call the doctor if,
- Feeding tube comes out, and you are unaware how to replace it
- Leakage around the tube
- Redness or irritation surrounding the skin area
- Blockage of the feeding tube
- Bleeding around the insertion site
Contact the provider if you:
- Have diarrhoea after feeding
- Severe pain
- Use a new medicine
- Have constipation
- Feel exhausted, shortness of breath and coughing frequently
- Have a swollen belly after feeding (1 hour)