Manometry and 24-hour pH study
Manometry and 24-hour pH study
Manometry
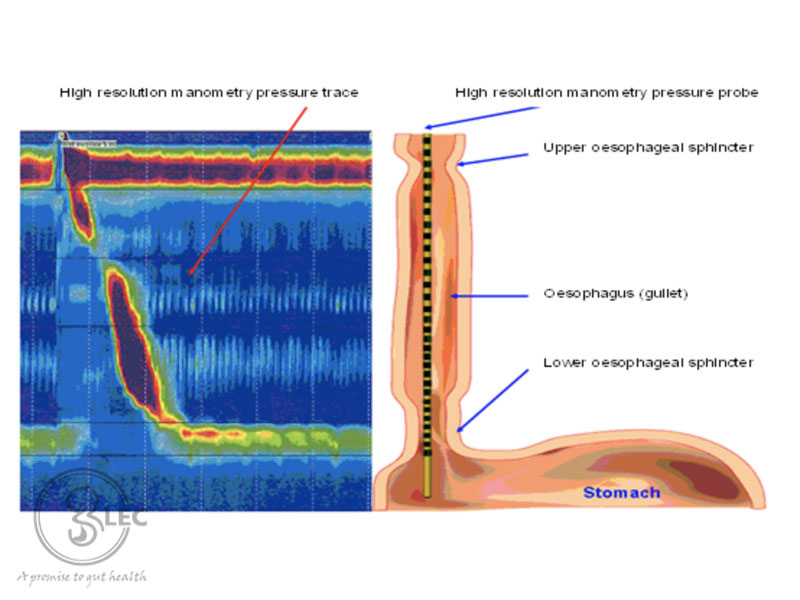
Manometry is a test that determines the pressure in different parts of the gastro-intestinal tract, such as the esophagus, lower esophageal sphincter, rectum, and anal canal.
Technique
A probe is used to assess the pressure, inserted via the anus or nose.
Types:
- Esophageal manometry
- Dysphagia – For example, in patients with motor disorders manometry is useful.
- Gastroesophageal reflux- (as low pressure of esophgaeal sphincter predisposes to acid reflux symptoms)
- Anorectal manometry
The esophgeal manometry examines the pressure within the esophagus with a sensing probe inserted through the nose
Indication
Anorectal manometry is the manometry technique where pressure is measured via the anus.
Indications
- Anal incontinence
- Chronic constipation because of neuronal diseases
24-hour pH study
24-hour pH study is indicated in patients with suspected gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Technique
- It is an ambulatory test, where pH probe passes from the nose to the lower esophagus.
- Probe remains in the specific position for an entire day.
- The probe is useful to determine any changes in the pH within the esophagus caused due to acidic reflux. pH probe records the episode of reflux from the stomach to esophagus that gets stored in a data recorder.
- These changes are later evaluated.