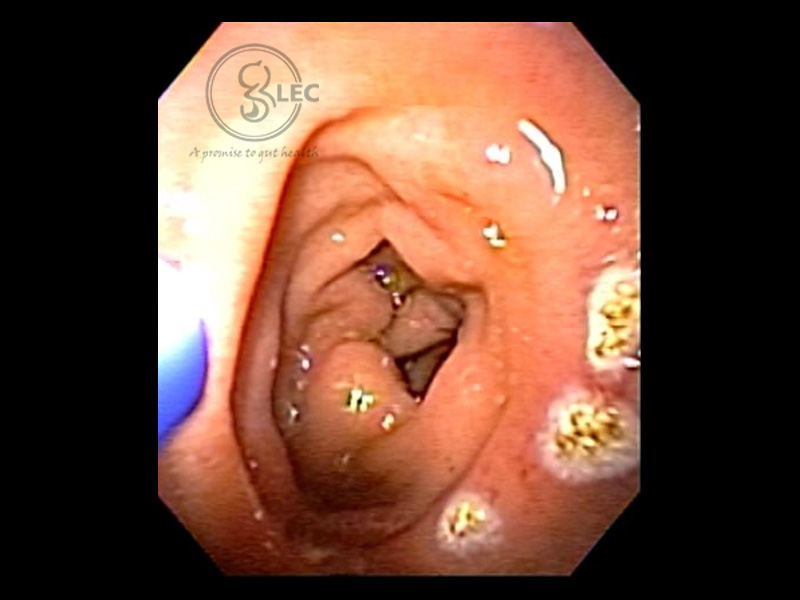
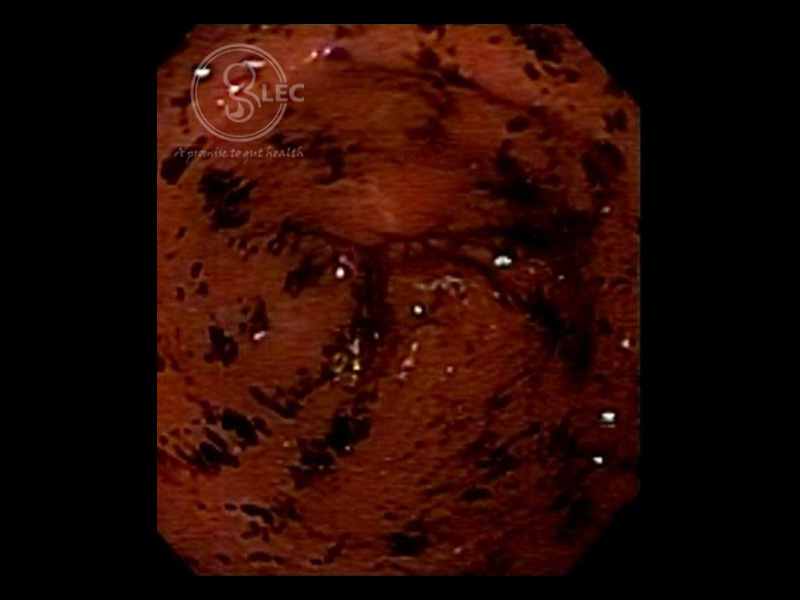
APC for GI Bleed
ARGON PLASMA COAGULATION FOR GI BLEED
Argon Plasma Coagulation or APC is a procedure used to control bleeding initiating from the lesions of gastrointestinal tract.
An effective approach to manage the tumor, if surgery is not a feasible option. Typically, it is quite challenging to manage gastrointestinal bleeding in case of cancer patients.
Thus, APC provides a superior approach where endoscopic hemostasis enables management of bleeding owing to non-neoplastic reason such as gastric antral vascular ectasia, radiation proctitis, and arterio-venous malformation.
Indications
- Angiodysplasias
- Colonic Polyps after Polypectomy
- Gastric antral vascular ectasia
- Radiation proctitis
- Esophageal Cancer
Technique
- An APC probe is used. The probe allows exchange of high frequency alternating current to the target site by using argon gas in a non-contact mode.
- Tissue desiccation occurs at the contact interface of the target site.
- Coagulation of bleeding areas is managed through high-frequency electric current that exits a flow of gases
- It is a safe procedure due to non-contact nature
- The best approach is to use a combination of Endoscopic banding ligation and argon plasma coagulation.
Challenges
Cancer patients who are susceptible to bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract have a higher risk for GIT haemorrhage. There is a high risk of severe bleeding in patients with metastatic tumors. APC is an effective technique that provides optimal results by a non-invasive approach.
In a brush like stroke, APC controls the oozing tissue.
Conclusion
APC is a safe, simple and effective method that can be used to manage GIT bleeding from the tumors. It promotes fast haemostasis and has the potential to control tumor-related gastrointestinal bleeding.