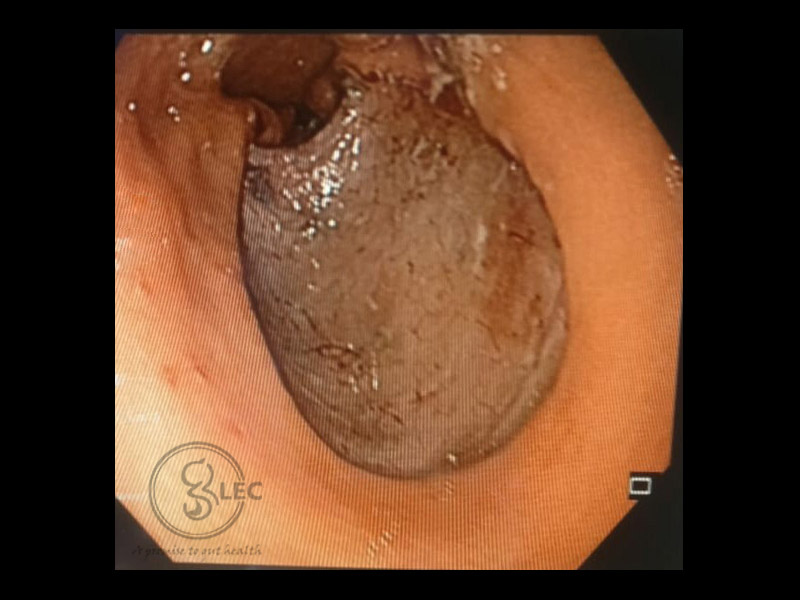
Gastric Tumor Removal
Gastric Tumor Removal
Tumors are an abnormal cellular mass, that may occur anywhere within the body. Stomach cancer is caused due to cell proliferation within the stomach lining, resulting in tumor development.
Risk factors predisposing to gastric tumor include:
- Obesity
- Excessive smoking
- Prior Stomach surgery (in case of an ulcer)
- Diet rich in salty foods
- People with Type-A blood group
- Genetic susceptibility
- Exposure to asbestos
- Chronic H.pylori infection within the gastric mucosa
- Autoimmune gastritis
- Long-term use of certain medications (e.g. proton pump inhibitors)
Severity increases as the size of tumor increases. For example, large and ulcerated tumors present with severe symptoms.
Signs and symptoms of stomach tumors
- Blood in stools
- Stomach pain
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Heartburn
- Feeling tired
- Yellowish eyes or skin
- Constipation or diarrhea,
- Nausea or vomiting
- Swelling inside the stomach
- Weight loss without any underlying reason
Ulcerated tumors have signs such as abdominal pain (mainly epigastrium), bleeding ulcers, and blood loss leading to anemia.
Large tumors may cause manifestations such as weight loss, nausea, vomiting, fullness, and feeling of bloating.
Diagnosis
Benign tumors do not present with symptoms and may remain undiagnosed for a prolonged period of time. Stomach polyps may cause darkened skin around the mouth.
A thorough physical examination is conducted.
Certain tests should be performed that includes:
- Upper endoscopy: A long tube with a camera is inserted in the throat. This allows examination of stomach.
- Blood tests: Determines any signs of cancer or tumor.
- CT scan: Evaluates the changes within the stomach.
- Biopsy: Small piece of stomach tissue is used to check the presence of any cancer cells.
- Upper GI series test: Patient drinks a chalking liquid called as barium, that forms a covering on stomach. This is visible on X-ray.
Treatment
- Surgery is the common approach for treating stomach tumors.
- Treatment of malignant tumor includes surgery or chemotherapy. Surgery helps to assess the kind and type of tumor.
- However, medications may be helpful in some cases.
- Other methods include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and biological therapy
Common approach is based on the TNM system.
- T means tumor and determines the size of the tumor.
- N means the spread of tumor cells to lymph nodes.
- M stands for metastasis
Surgery is useful to improve the treatment outcomes.
Diagnostic tumor removal:
- A tissue sample is obtained to assess any abnormalities.
- Biopsies can of be various types that can vary depending on the lesion such as excisional biopsy, incisional biopsy, and needle biopsy.
Therapeutic tumor removal:
- It involves surgical removal of the entire tumor.
- Removal of tumor helps to reduce patient’s pain and other signs associated with this problem.
- Majority of the tumors resolve and have less tendency to regrow. Therefore, regular monitoring is necessary to assess the recurrence and timely determine any changes in cell growth.