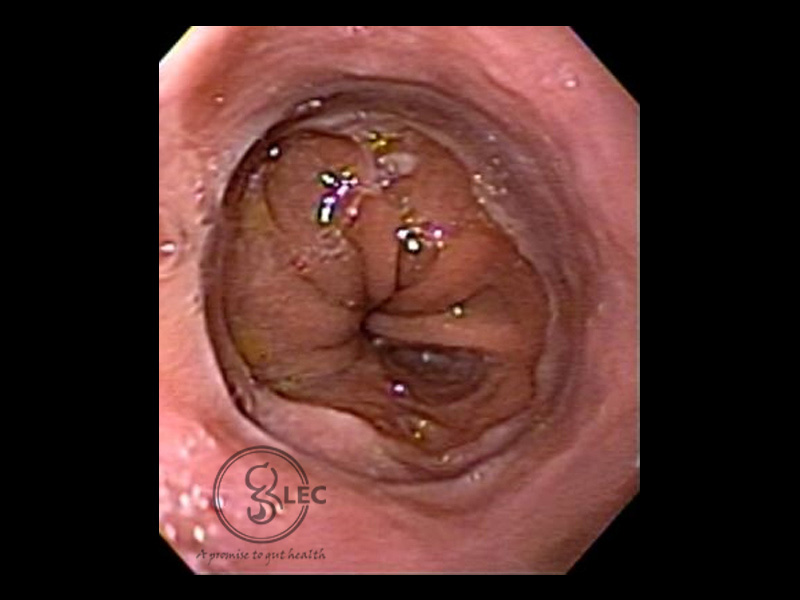
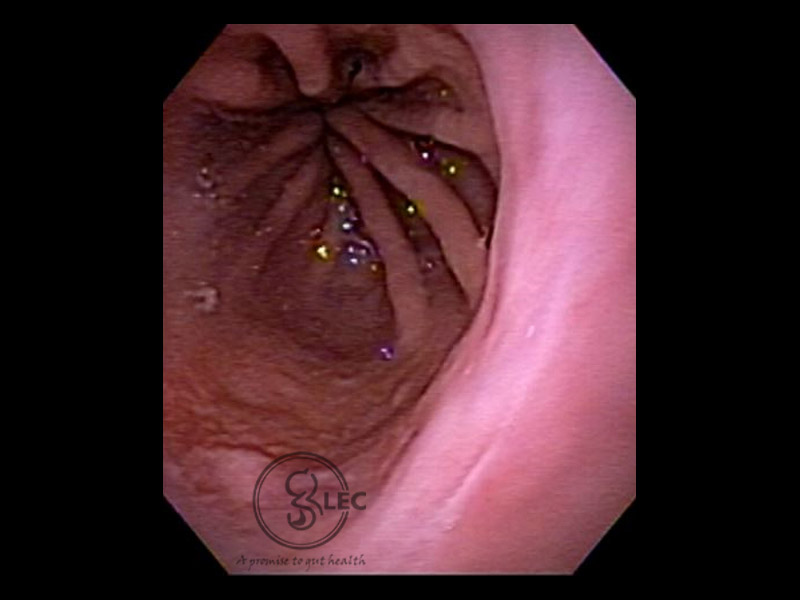
Gastroesophageal Reflux
Gastroesophageal Reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) is caused when the normal anti-reflux barrier is impaired in the lower esophageal sphincter. One of the most common factors that that causes severe GERD is hiatus hernia as it affects the normal functions of the lower esophageal sphincter Patient may present with mild heartburn with normal endoscopic findings. There can be absence of esophageal mucosal disease, or in some situations patient may present with
esophageal ulcerations, dysphagia, bleeding, and stricture. Prolonged GERD can worsen the situation causing Barrett’s esophagus, a risk factor for cancer and esophageal dysplasia.
Symptoms
- Retrosternal burning pain
- Odynophagia- pain during eating
- Dysphagia-difficulty in eating
- Upper GI bleed
Diagnosis
- Patients presenting with classic GERD symptoms are easily diagnosed and no specific testing is required.
- Patients presenting with severe symptoms (dysphagia and bleeding) require endoscopy to establish the diagnosis and rule out other factors.
- Other tests include such as barium swallow, maonometry and 25-hour pH testing.
Treatment
- Lifestyle modification
- Avoid smoking and alcohol
- Avoid tight fitting clothes
- Raise the head end of bed
- Exercise to lose weight
- Avoiding snacking at night time
- Avoiding Tea/coffee
- Avoid aerated drinks
Medications
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPI) and prokinetic agents are helpful in controlling the symptoms
Surgery
- Fundoplication is the procedure that helps to manage the physiological processes responsible for GERD
Indication for surgery
- Patients responsive to PPI, but do not wish to continue long-term medications
- Young patients with recurrent stricture