Colonic Polyps and Cancer
Colonic Polyps and Cancer
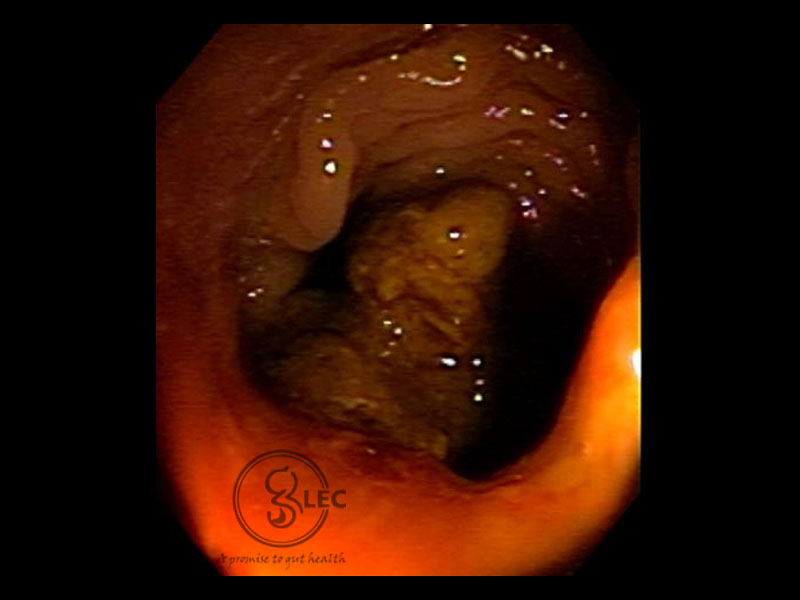
Colonic polyp
A polyp is a discrete tissue mass that protrudes into the lumen of the bowel.
Polyps are categorized into neoplastic polyps and non-neoplastic polyps
Neoplastic polyps
- Adenoma
Non-neoplastic polyps
- Hyperplastic polyps
- Inflammatory polyps
- Juvenile polyps
- Peutz Jeghers polyps
Adenoma
Adenomas are benign polyps, categorized into two types, tubular and villous adenomas.
Polyps > 2 cms, and those with villous structural morphology have a higher possibility to transform to malignancy.
Polyps <5 mm are known as diminutive polyps. Polyps have no potential to transform into malignancy.
Risk factors
- Inherited susceptibility
- Excessive dietary intake of low fiber and fat
Clinical features
Most of the polyps are asymptomatic
- Abdominal pain
- Rectal bleeding
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Colonic obstruction
Detection
- Colonoscopy is indicated for diagnosing polyps
Treatment
- Adenomas that do not encroach deeper layers require endoscopic management.
- Resected polyp should undergo histopathologic examination to confirm the complete resection
- A polyp that invades deeper layers should be managed surgically
Colon cancer
Colon cancer is a major factor for morbidity and mortality
Risk factors
- High fat low fiber diet
- Smoking
- Colorectal adenomas polyposis syndromes
- Family history of colorectal cancer
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn’s disease
Symptoms
- Tumors that are present on the right side of the colon have a large size. It presents as chronic bleeding in addition to a palpable mass.
- Tumors that are present on the left side of the colon have different clinical manifestations such as changes in bowel habits, anemia, abdominal pain, and chronic bleeding.
Diagnosis
- Colonoscopy helps in confirmation of diagnosis
- Biopsy identifies suspected growth based on the histopathological confirmation
Staging
- CECT abdomen determines distant metastasis
Treatment
- Surgery is the main treatment modality for colon cancer
- Patients with advanced disease (such as disease extending beyond serosa, liver metastasis) are recommended chemotherapy