GIST and Lymphoma
GIST and Lymphoma
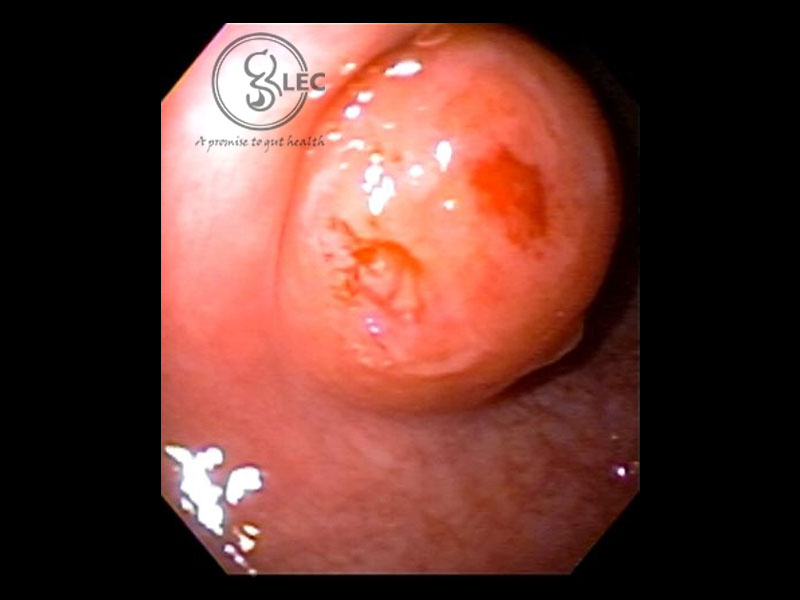
GIST (Gastrointestinal stromal tumor)
GIST most commonly affects the stomach. Other sites include the esophagus, small intestine, and rectum.
Clinical presentation
- Asymptomatic lesions are usually detected by CT scan or endoscopy
- GI bleeding presents as black colored stools and hematemesis
- Abdominal pain
- Obstructive features include dysphagia, abdominal distension, severe pain abdomen, and recurrent vomiting
Diagnosis
Diagnostic tests include:
- CECT abdomen
- Endoscopy and endoscopic ultrasound
- PET scan to assess distant metastasis
Treatment
- Small GIST requires follow-up
- Large tumor in absence of metastasis requires surgery
- Chemotherapy with imatinib and sunitinib is indicated for unresectable tumors, and when the surgical approach is not feasible.
Gastric Lymphoma
Gastric lymphoma represents 3-5 % of all gastric tumors. The most common extranodal site of lymphoma is the stomach.
Marginal zone B cell lymphoma is called as MALT lymphoma. It is the most common lymphoma of the stomach.
The main causative factor for this lymphoma is chronic H pylori infection that causes chronic gastritis.
Clinical features
- Dyspepsia
- Epigastric pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Early satiety
- GI bleeding
- Fever
- Weight loss
Diagnosis
Endoscopy identifies the lesions, and endoscopic findings are
- Erythema
- Erosions
- Ulcers
- Growth
A biopsy is taken from suspicious areas
CT and EUS indicated to determine the extent of diseases and metastasis
Treatment
- The initial stage of the disease can be managed by H Pylori eradication.
- Patients with advanced disease should undergo chemotherapy treatment
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
H pylori is associated in the pathogenesis of the lymphoma, however the relationship is still unclear.
Clinical symptoms
- Epigastric pain
- Dyspepsia
- A large tumor that causes obstruction
- An ulcerated mass that may bleed
Diagnosis
- Upper GI endoscopy and biopsy are important for diagnosing the disease.
- Endoscopic findings reveal ulceration and a large tumor
- The common sites include body and antrum
- CT/PET and EUS are useful for tumor staging
Treatment
- The main treatment modality is chemotherapy with or without radiotherapy